Accelerating Accessibility Policy Work Program
1982
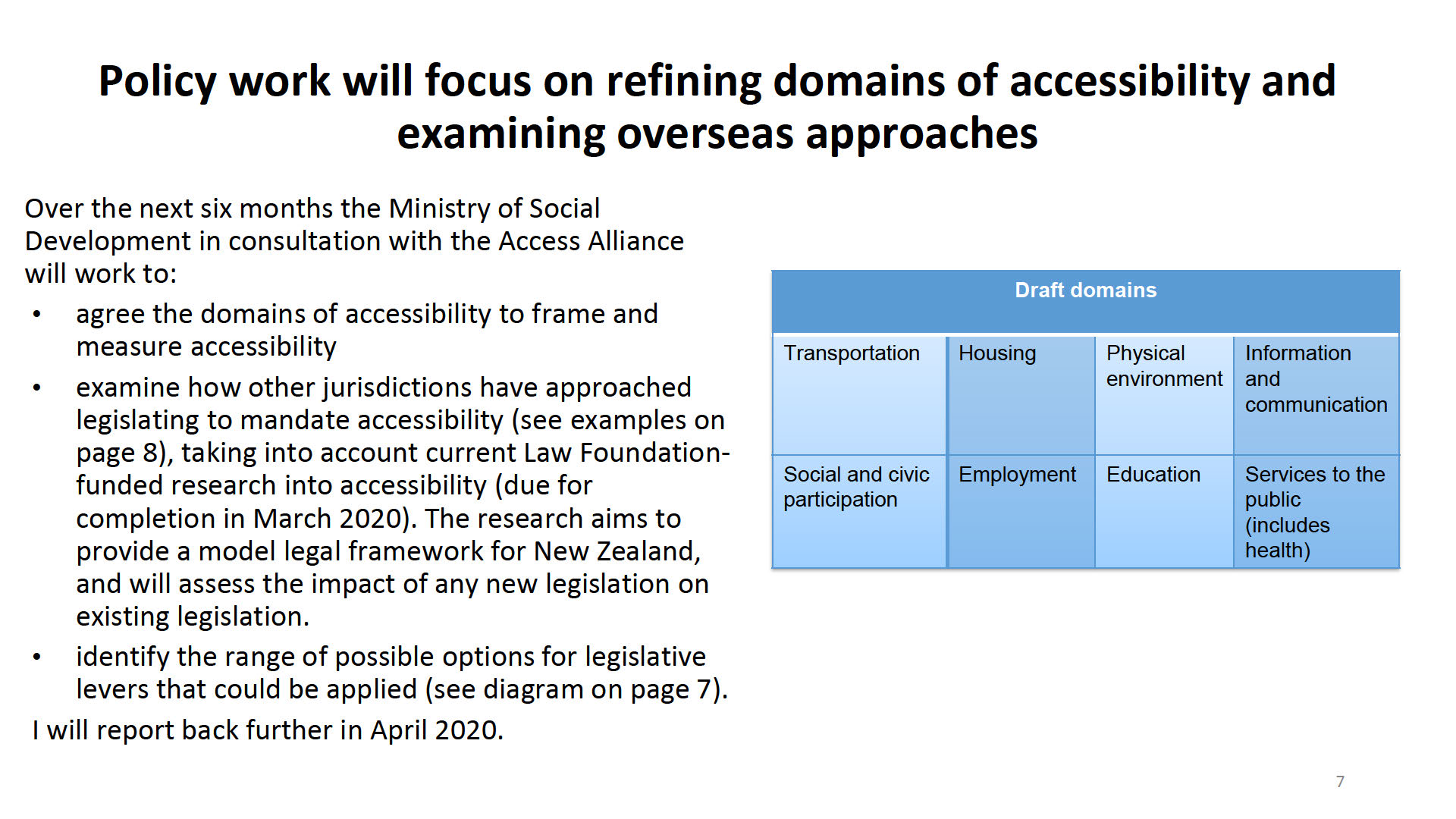
me:
Interim Update
Act
How to achieve full accessibility in Aotearoa New Zealand –
a pathway forward
Information
Official
the
under
1
Released
Our Opportunity
1982
Act
Accessibility means all New Zealanders living
independently and participating fully in all areas of life with
confidence and dignity
➢ More than a million New Zealanders have visible and invisible disabilities.
Information
➢ Accelerating accessibility benefits many other people including seniors,
carers of young children, people for whom English is a second language, and
Official
people with temporary injuries, as well as their friends and families.
the
➢ Accessibility is about navigating more than physical environments. It’s also
about access to services like public transport, entertainment, banking, and
under
information and communication.
➢ The Access Alliance has developed a description of what Aotearoa New
Zealand would look like if it were the most accessible country in the world.
Released
What do stakeholders think about accessibil
1982
ity?
Act
The Ministry of Social Development and the Access Alliance worked
together to host discussions with a range of stakeholders to listen to
their perspectives on accessibility
Key themes:
Information
➢
No common understanding of ‘full
➢ A large cultural and attitudinal shift,
accessibility’.
as part of meaningful change, is
needed.
➢
There is support for change.
➢
Official Some agreed markers of success
➢
The problem we are aiming to address
are inclusiveness, flexibility, and a
is multi faceted.
the
holistic, people-centred approach.
➢
There was no support for staying with
➢ Stakeholders support government
the status quo.
involvement being a combination of
under
➢
Stakeholders provided feedback on
legislation, awareness raising and
how we should frame the way we think
educational action.
about and measure accessibility.
3
Released
1982
Clear support for legislation, coupled with awareness
Act
raising and education
➢ Stakeholders support government involvement being a combination of
legislation, awareness raising, and education.
Information
➢ Legislation is a powerful driver of behavioural change.
➢ Stakeholders support some form of legislation, for these reasons:
Official
•
the compulsion of law can drive change
•
legislation would demonstrate we
the are serious
•
legislation would help organisations do the right thing
•
new overarching legislation would overcome the issue of different pieces
under
of legislation that don’t interact well.
4
Released
Legislation, coupled with awareness raising
1982
and
education
Act
Stakeholders thought without legislation, there will be no substantive progress, but it needs to
go hand in hand with considered design, awareness raising and education for organisations
and business
➢ Business told us that “it’s about creating an
➢ Legislation needs to be accompanied by
Information
environment to progress the organisations in
support for people and businesses. This could
the right direction. New Zealand isn’t quite
include:
inclusive for all communities yet.”
• general public awareness and/or
➢
Official
Legislation alone will not solve all issues and
educational campaigns
will not mean everyone is in support.
• a segmented approach, tailored to specific
the
➢ Legislation can take a number of forms:
audiences
• amendments to primary legislation
• support for businesses or organisations to
•
under
amendments to secondary legislation,
make change.
regulations, or local bylaws
• new overarching legislation.
5
Released
Options for change can be a mix of legislative and other approaches and can
1982
reinforce each other
Act
Legislation
Support
More intensive
Support and assistance for
New overarching legislation
options
businesses and groups
governing the introduction of
wanting to adopt accessible
compulsory standards
Information practices
Amendments to existing
Moderate
Specific sector-based
Official
primary legislation, such as
options
education on relevant issues
the Building Act, to better
and best practice for
the
enforce accessibility
accessibility
under
Amendments to existing
secondary legislation,
Less intensive
General public awareness
regulations, or local bylaws
campaign and education
options
6
Released
1982
Act
Information
Official
the
under
Released
1982
Overseas examples
Act
Ontario, Canada
Norway
• The Accessibility for Ontarians with
• The Anti-Discrimination and Accessibility Act
Disabilities Act 2005 (AODA) specifies four
of 2008 made lacking accessibility a form of
accessibility domains. Mandatory standards
discrimination.
under each domain are gradually developed
• The Act includes safeguards against
and introduced by regulation.
Information
discrimination and an obligation to use
• Standards are developed by co-design
universal design principles.
reference groups, including disabled
• The Act refers to sector legislation as well
people, industry experts and officials.
as specific regulations.
• Once developed, a standard is referred to Official
• Many of the Act’s provisions become
the responsible Minister for approval (and a
enforceable through regulations specifying
standards committee later reviews). This
detailed accessibility requirements.
the
process acts as a safeguard.
• Like Ontario, there is an end goal of 2025.
• Five codes and standards have been set so
far. AODA seeks to reach a fully accessible
• This has been accompanied with a
Ontario by 1 January, 2025.
widespread cultural shift, where
under
inaccessibility is met with fines and bad
• There is widespread support for Ontario’s
publicity.
model both within the province and from
abroad.
Released
1982
Next steps
Act
The Ministry of Social Development will work to clarify feasible options for
a policy approach that combines legislative change with education and
awareness raising, and support for organisations and businesses in close
consultation with the Access Alliance.
•
Information
This will involve:
•
identifying priorities and key elements to include in the policy approach
•
agreeing on accessibility domains to frame and measure accessibility (see page 6)
Official
•
looking at the performance of existing regulatory mechanisms to determine what shortfalls
the
exist and need to be resolved (taking into consideration the legal research underway)
•
considering implementation issues
•
estimating quantifiable costs, and the long-term benefits and cost savings
under
•
assessing risks and mitigations.
Released

1982
Act
Information
Official
the
under
Released

1982
Act
Information
Official
the
under
Released

1982
Act
Information
Official
the
under
Released



